Your First Experiment¶
Validate service level objectives (SLOs) for an app
Problem: You have a Kubernetes app. You want to verify that it satisfies latency and error rate SLOs.
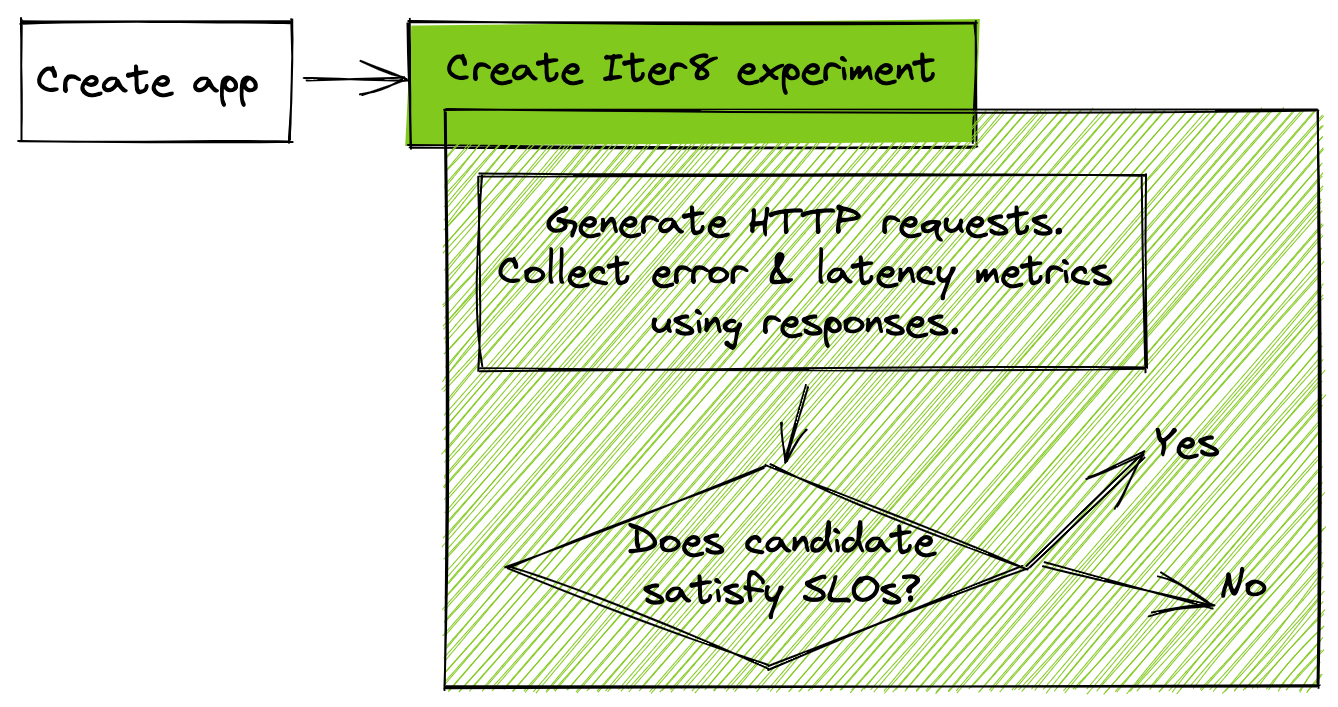
Solution: In this tutorial, you will launch a Kubernetes app along with an Iter8 experiment. Iter8 will validate that the app satisfies latency and error-based objectives (SLOs) using built-in metrics. During this validation, Iter8 will generate HTTP GET requests for the app.
Preview:
Setup Kubernetes cluster and local environment
- Setup Kubernetes cluster
- Install Iter8 in Kubernetes cluster
- Get Helm 3.4+.
- Get
iter8ctl - Fork the Iter8 GitHub repo. Clone your fork, and set the
ITER8environment variable as follows.export USERNAME=<your GitHub username>git clone git@github.com:$USERNAME/iter8.git cd iter8 export ITER8=$(pwd)
1. Create app¶
The hello world app consists of a Kubernetes deployment and service. Deploy the app as follows.
kubectl apply -n default -f $ITER8/samples/deployments/app/deploy.yaml
kubectl apply -n default -f $ITER8/samples/deployments/app/service.yaml
1.a) Verify app is running¶
# create curl pod and get shell
kubectl run curl --image=radial/busyboxplus:curl -i --tty --rm
# curl app
curl hello.default.svc.cluster.local:8080
Curl output will be similar to the following (notice 1.0.0 version tag).
Hello, world!
Version: 1.0.0
Hostname: hello-bc95d9b56-xp9kv
# exit from curl pod
exit
2. Launch Iter8 experiment¶
Deploy an Iter8 experiment for SLO validation of the app as follows.
helm upgrade -n default my-exp $ITER8/samples/slo-validation \
--set URL='http://hello.default.svc.cluster.local:8080' \
--set limitMeanLatency=50.0 \
--set limitErrorRate=0.0 \
--set limit95thPercentileLatency=100.0 \
--install
The above command creates an Iter8 experiment that generates requests, collects latency and error rate metrics for the app, and verifies that the app satisfies mean latency (50 msec), error rate (0.0), 95th percentile tail latency (100 msec) SLOs.
2.a) View manifest and values¶
View the manifest created by the Helm command, the default values used by the Helm chart, and the actual values used by the Helm release using the following instructions.
View experiment manifest using these instructions
helm get manifest -n default my-exp
Your manifest created by will be similar to the following.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | |
The metrics/collect task highlighted above is responsible for generating and sending HTTP requests to the app's API endpoint, receiving responses, and creating latency and error-related metrics. The objectives stanza describes the SLOs that the app needs to satisfy in order to be declared a winner.
View default values used by the Helm chart
helm show values $ITER8/samples/slo-validation
This will display the defaults in the Helm chart's values.yaml file as follows.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
View values set in the Helm release
helm get values my-exp --all
This will display the all the values set in the Helm release as follows.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
3. Observe experiment¶
The iter8ctl CLI makes it easy to observe experiment progress and outcomes.
3.a) Assert outcomes¶
Assert that the experiment completed and found a winning version. Wait 20 seconds before trying the following command. If the assertions are not satisfied, try again after a few seconds.
iter8ctl assert -c completed -c winnerFound -n default
3.b) Describe results¶
Describe the results of the Iter8 experiment.
iter8ctl describe -n default
Sample experiment results
****** Overview ******
Experiment name: slo-validation-1dhq3
Experiment namespace: default
Target: app
Testing pattern: Conformance
Deployment pattern: Progressive
****** Progress Summary ******
Experiment stage: Completed
Number of completed iterations: 1
****** Winner Assessment ******
> If the version being validated; i.e., the baseline version, satisfies the experiment objectives, it is the winner.
> Otherwise, there is no winner.
Winning version: my-app
****** Objective Assessment ******
> Whether objectives specified in the experiment are satisfied by versions.
> This assessment is based on last known metric values for each version.
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------+
| METRIC | CONDITION | MY-APP |
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------+
| iter8-system/mean-latency | <= 50.000 | true |
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------+
| iter8-system/error-rate | <= 0.000 | true |
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------+
| iter8-system/latency-95th-percentile | <= 100.000 | true |
+--------------------------------------+------------+--------+
****** Metrics Assessment ******
> Last known metric values for each version.
+--------------------------------------+--------+
| METRIC | MY-APP |
+--------------------------------------+--------+
| iter8-system/mean-latency | 1.285 |
+--------------------------------------+--------+
| iter8-system/error-rate | 0.000 |
+--------------------------------------+--------+
| iter8-system/latency-95th-percentile | 2.208 |
+--------------------------------------+--------+
| iter8-system/request-count | 40.000 |
+--------------------------------------+--------+
| iter8-system/error-count | 0.000 |
+--------------------------------------+--------+
3.c) Debug¶
The iter8ctl debug command is especially useful in situations where the experiment failed to complete successfully, or produces an unexpected outcome (such as failure to find a winning version).
# print Iter8logs at priority levels 1 (error), 2 (warning), and 3 (info)
iter8ctl debug --priority 3 -n default
Sample output from iter8ctl debug
Debugging experiment slo-validation-rsuq7 in namespace default
source: task-runner priority: 3 message: metrics collection completed for all versions
4. Cleanup¶
helm uninstall -n default my-exp
kubectl delete -n default -f $ITER8/samples/deployments/app/service.yaml
kubectl delete -n default -f $ITER8/samples/deployments/app/deploy.yaml
Reuse with your app
-
Reuse the above experiment with your app by replacing the
helloapp with your app, and modifying the Helm values appropriately. -
Try other variations of SLO validation that involve: